Virtual machine may be a great instrument for dealing with issues related to data protection and safe program delivery, code testing, software performance research. However, the use of such technologies order to obtain financial services may indicate user's malicious intentions and, therefore, high risk for the business.
We have spotted rising number of virtual machines in application flow recently, thus, we would like to share our statistics data on virtual machines percentage ratio in various regions as well as to highlight the most effective approaches to identify this threat.
What is a virtual machine and how it is related to risk assessment technologies?
The core of our fraud prevention approach is careful and accurate device authentication, taking into account various parameters of any device, its environment and use. Virtual machines detection has become very relevant issue recently, for we have spotted a higher degree of virtual devices use in the regions of our presence.
What is a virtual device or machine? It is any type of device (PC, tablet PC, smartphone etc.) created with special software or program code. In fact, such device doesn't differ from any physical computer/laptop/smartphone or even a server. It also has a processor unit, memory module, data and file storages, and it also can connect to the Internet if needed. However while real computers have physical storage system, memory modules and microprocessor chipsets, virtual machines or software-defined computers exist only as a code.
Virtual device make company's IT-infrastructure operations much easier and also increases productivity due to resource optimization. For example, several servers may be combined into one virtual machine and vice versa - one can split one powerful machine into several smaller servers, depending on the current needs of the company. However, the use of such technologies in financial products and services obtaining may indicate user's malicious intentions and, therefore, may lead to high risk for the business.
There are several types of virtual machines. The first one may be described as various software solutions, which bear signs of virtualization. For example, private mode in a browser or LockDown mode on a device. Such mechanisms are often used to protect users privacy. Solutions with signs of virtualization, as a rule, do not carry significant risks, but sometimes the risk of such software solutions can be above average.
The second type can be attributed to the most dangerous ones - the actual virtual machine - a system that emulates computer hardware (actually, it may be both software and hardware). It is necessary to distinguish these two types of virtual machines in order to deal with them in a more effective way.
Virtual machines average fraud level
As part of the analysis of virtual machines detection, we reviewed the statistics on a selection of variables: to be more precise, we estimated the average risk not only for virtual machines, but for all records.
Based on our analysis, the average risk across all applications with the signs of virtual machines presence was on average 1.3-1.5 times higher than the average risk across all records. At the same time, those companies that do not pay attention and do not filter virtual machines have a default rate 2.5-3 times higher than average.
Also we assessed growth dynamics of the virtual machines use in various regions over the past 6 months.
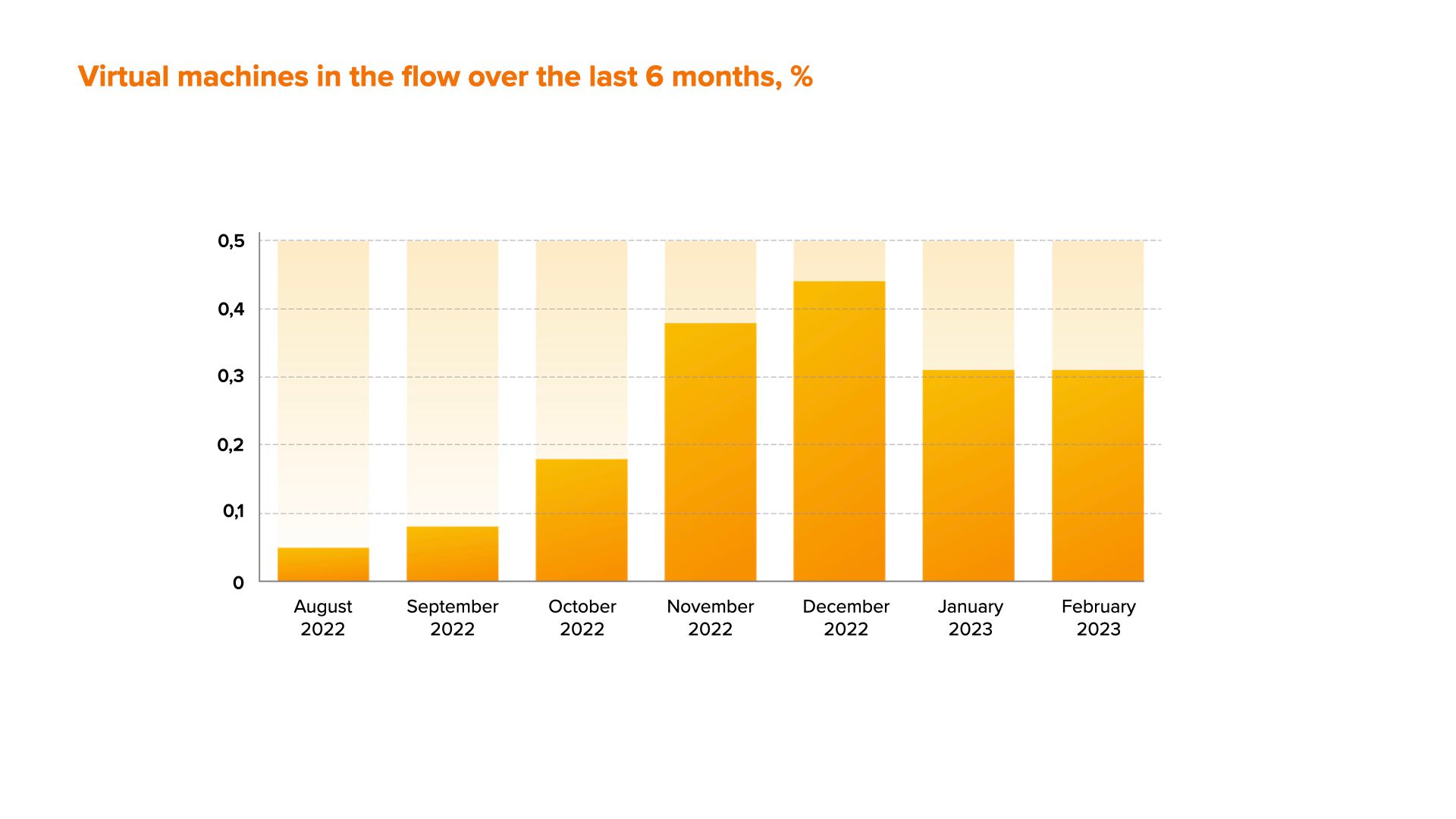
Over the past six months we noticed an increase in the use of virtual machines. December surge is quite easy to explain: the amount of online-fraud attacks usually rises dramatically before the holidays along with the consumers’ need for shopping and, as a result, the need for additional credit means.
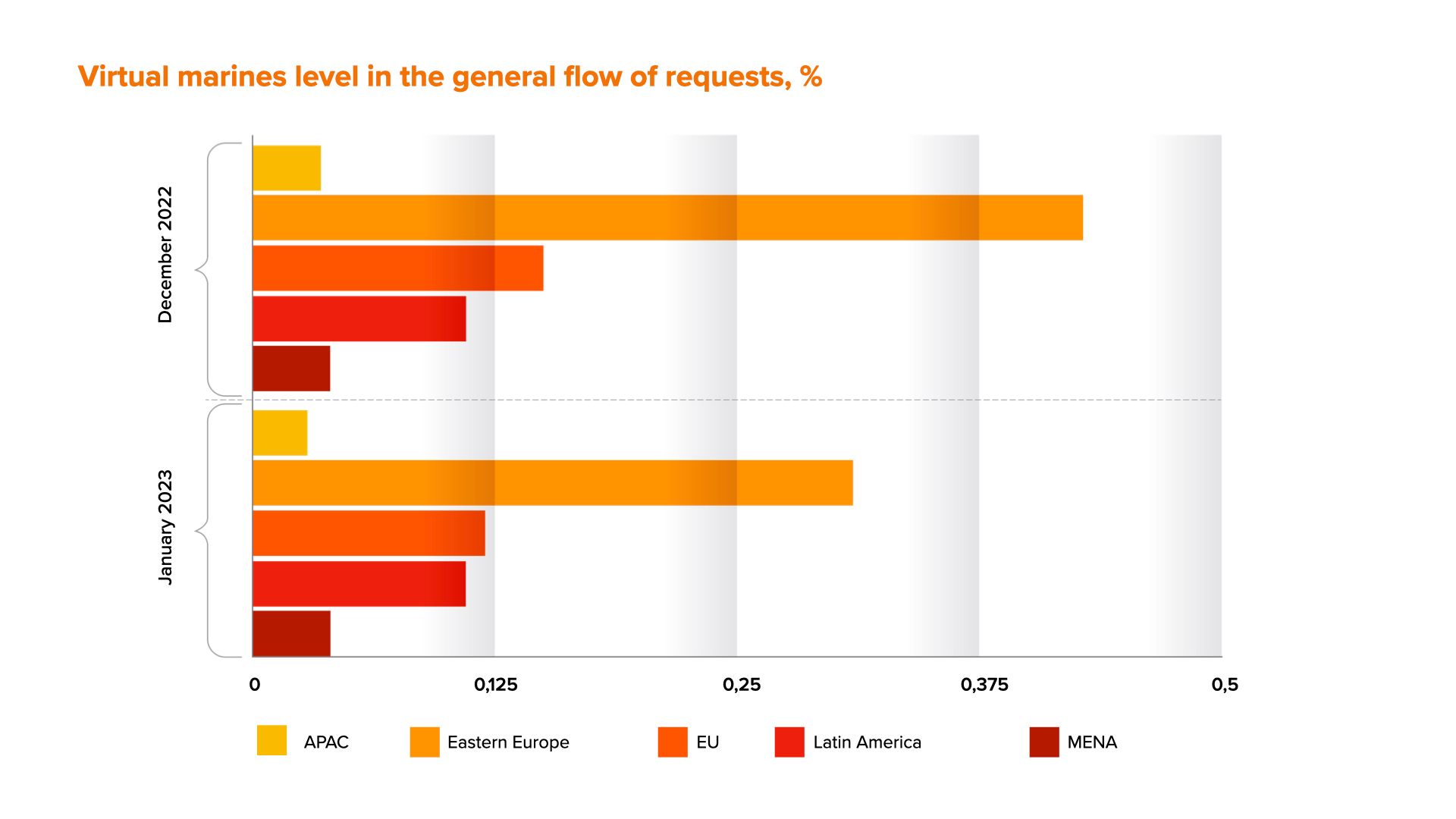
In addition to that, we analyzed the distribution of traffic by virtual machines over the past 2 months with a regional breakdown. On the graph below you can see the percentage of applications with signs of virtual machines use from the total flow of applications:
What are the main approaches to virtual machines detection?
The classic method to identify virtual machines is based on operating system characteristics analysis. However, this method is not available for a web application. In this case a number of solutions and methods are also available. Nevertheless they also a range of drawbacks, such as Type I and Type II significant errors:
- Virtual machines detection through significant anomalies. The advantage of this approach is that it has the lowest degree of Type II error:
a. Rendering anomalies;
b. Anomalies of screen and graphic properties;
c. RAM properties and some other functions anomalies;
2. Virtual machines detection using performance tests:
a. Graphic performance (for example, FPS, rendering graphics characteristics);
b. Operating memory performance;
c. Hard drive performance;
d. Sound card performance and other properties;
- Identification of virtual machines through analysis of the installed software integrity. This direction is the most promising and effective for web applications due to the fact that virtual machines significantly differ in content/functionality from real devices.
#Some final thoughts
Naturally, in antifraud and risk management there is no single and universal approach that would solve any problem and give 100 percent result - every expert is in constant search of a balance between data value and a stable approach. Based on our experience, the most effective anti-fraud and risk management solutions should be able to detect risk in real time, have high data value in order to improve decision-making system, as well as analyze user behaviour and identify hidden correlations.